Best Vitamin D Supplements of 2024
We analysed hundreds or Vitamin D supplements that are currently available on the market and our Top 7 picks are:
1. NATURELO Organic Plant-Based Vitamin D
 |
Contents: 180 capsules Amount per capsule: 2500 IU Vitamin D source: Organic Lichen Absorption co-factors: some Made in: U.S.A. MSRP: $22.95 Price per 5000 IU: $0.26 |
2. Garden of Life Vitamin Code RAW D3
 |
Contents: 120 capsules Amount per capsule: 2000 IU Vitamin D source: Lanolin/Yeast Absorption co-factors: some Made in: U.S.A. MSRP: $34.95 Price per 5000 IU: $0.73 |
3. MegaFood Vitamin D3
 |
Contents: 90 tablets Amount per tablet: 2000 IU Vitamin D source: Lanolin/Yeast Absorption co-factors: some Made in: U.S.A. MSRP: $35.50 Price per 5000 IU: $0.99 |
4. Country Life Vegan D3
 |
Contents: 60 softgels |
5. Nature's Plus Source of Life Garden Vitamin D3
 |
Contents: 60 capsules Potency per capsule: 2500 IU Vitamin D source: Organic mushrooms Absorption co-factors: not included Made in: U.S.A. MSRP: $14.90 Price per 5000 IU: $0.50 |
6. Thorne Research D-5000
 |
Contents: 60 capsules Amount per capsule: 5000 IU Vitamin D source: Lanolin Absorption co-factors: not included Made in: U.S.A. MSRP: $11.50 Price per 5000 IU: $0.19 |
7. Solgar Vitamin D3 Cholecalciferol
 |
Contents: 100 capsules Amount per capsule: 2200 IU Vitamin D source: Lanolin Absorption co-factors: not included Made in: U.S.A. MSRP: $12.98 Price per 5000 IU: $0.29 |
Why do I need to take vitamin D supplements?
All systems in our bodies need vitamin D, so a deficiency in this essential nutrient often contributes to the development of disease. For example, children who are severely deficient in vitamin D develop rickets, while adults who do not have adequate vitamin D in their system are likely to experience a bone softening condition known as osteomalacia.
Clinical research shows that mild vitamin D deficiency predisposes people to a variety of chronic diseases, such as:
- Osteoporosis
- Impairments in immune functioning
- Autoimmune diseases, such as juvenile diabetes and multiple sclerosis
- Cancers of the breast, lung, colon, and prostate, as well as lymphoma
- Hypertension
- Complications in pregnancy
- Cardiovascular disease
Since all these conditions are linked to vitamin D deficiency, you need to ensure that you maintain sufficient levels of this vitamin in your system.
How did you determine the best vitamin D supplements?
We've been analysing vitamin supplements for years. As a result we have built a database of manufacturers that consistently deliver high quality products. We picked the best vitamin D supplements you see above in part based on the reputation score of the manufacturer. We also looked at test analysis reports provided by third-party testing labs in order to confirm that each of the above products meets our quality standards.
How does vitamin D work?
You can think of Vitamin D as a key that unlocks your DNA. It essentially tells your genes what to do. The genes are the computer that runs your body. When a cell wears out, it's your genes that regulate the production of a new cell. When your body doesn't have enough of one enzyme or has too much of a certain protein, it is your genes that need to increase or decrease the production of that enzyme or that protein.
2000 of the genes in your body are waiting for an adequate amount of vitamin D so that they can be told what to do. Without it the body cannot signal those genes to act as they should.
How do I check my vitamin D level?
Besides going to your doctor for a blood draw and lab test, you can join the D*action Project, which is a global public health initiative that aims to solve the worldwide epidemic of vitamin D deficiency. One of the projects sponsors, GrassrootsHealth, offers test kits with laboratory analysis completed by ZRT Labs. The price of each individual test is $60.00.
What is the recommended daily dose of vitamin D?
To maintain the recommended concentration of 25(OH)D (vitamin D), you need to take in at least 4000 IU/day. Between skin exposure to sunlight and food sources, the average person’s intake of vitamin D is about 2000 IU/day, which is half of what we need to stay healthy. To make up this difference, most people need to take vitamin D supplements that provide 1000 IU to 3000 IU per day.
To determine the exact dosage of vitamin D supplements you need, the first step is find out what your current level of vitamin D is by having it tested. Once you have this baseline measure of vitamin D, then use this chart to determine what daily dose of vitamin D you need.
Table 1: How much vitamin D you need to supplement with?
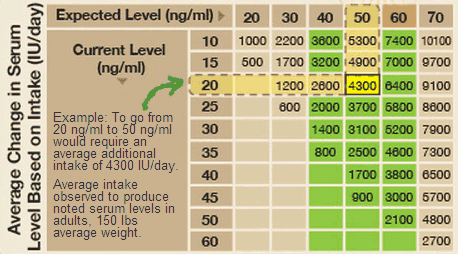
Source: Grassroots Health
Using the table above you can see how if you have a target vitamin D blood serum level of 50 ng/ml, but currently your vitamin D concentration level is only 20 ng/ml, then you need to supplement with 4300 IU of vitamin D per day.
What is the ideal vitamin D blood serum concentration?
A group of 42 researchers and practitioners gathered by GrassrootsHealth all agreed a vitamin D blood serum concentration range of 40 to 60 ng/ml is the ideal range needed to maintain good health.
This consensus is supported by a research study of native Equatorial African tribes that don't wear clothes and are exposed to strong sunlight all day long. When the scientists conducted blood tests to determine the vitamin D levels of individuals in these tribes, they found their levels to be around 48ng/ml on average. The authors concluded that since DNA studies have shown that the ancestors of early humans originally come from this area of Africa, the vitamin D concentration of 48 ng/ml is most likely the natural optimal level of vitamin D for humans.
Why is the RDA for vitamin D so much lower?
The US Institute of Medicine set the recommended daily allowance (RDA) for vitamin D at 600 IU/day for people under the age of 70 and 800 IU/day for adults over the age of 70.
Historically the medical community did not consider vitamin D to be crucial for optimal health. They only acknowledged that some vitamin D was needed to help the body use calcium to maintain the strong teeth and bones. During the last decade, however, many studies conducted throughout the world have discovered the importance of vitamin D in maintaining overall health. This research provides substantial evidence that we need much more than the RDA of vitamin D to stay healthy.
Is this backed up by real research?
Yes, here is a summary of the latest research findings:
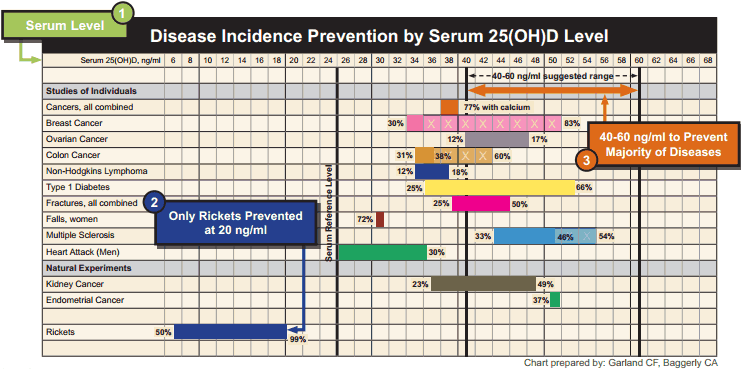
- 77% of all cancer cases can be prevented with vitamin D serum of 38 ng/ml
- 83% of Breast Cancer cases can be prevented with vitamin D serum of 50 ng/ml
- 17% of Ovarian Cancer cases can be prevented with vitamin D serum of 47 ng/ml
- 60% of Colon Cancer cases can be prevented with vitamin D serum of 42 ng/ml
- 18% of Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma cases can be prevented with vitamin D serum of 37 ng/ml
- 66% of Type 1 Diabetes cases can be prevented with vitamin D serum of 52 ng/ml
- 50% of Bone Fractures can be prevented with vitamin D serum of 44 ng/ml
- 54% of Multiple Sclerosis cases can be prevented with vitamin D serum of 54 ng/ml
- 30% of Heart Attack cases in men can be prevented with vitamin D serum of 35 ng/ml
- 49% of Kidney Cancer cases can be prevented with vitamin D serum of 47 ng/ml
- 37% of Endometrial Cancer cases can be prevented with vitamin D serum of 50 ng/ml
Table 2: Disease Incidence Prevention by Serum 25(OH)D Level
Which organizations participate in this research?
Research teams from the following organizations based in United States, Canada, United Kingdom, Germany, Austria, Japan and New Zealand are currently at the forefront of vitamin D research:
- Harvard University (United States)
- Oxford University (United Kingdom)
- University of California, Los Angeles (United States)
- University of Toronto (Canada)
- Boston University (United States)
- Institute Vitamin Delta (Germany)
- Creighton University (United States)
- Emory University (United States)
- International Medical Center of Japan (Japan)
- University of California, San Diego (United States)
- Linus Pauling Institute (United States)
- McGill University (Canada)
- Massachusetts General Hospital (United States)
- Medical University of Graz (Austria)
- Medical University of South Carolina (United States)
- University of Auckland (New Zealand)
- Roswell Park Cancer Institute (United States)
- Sunlight, Nutrition and Health Research Center (United States)
- University at Albany-SUNY (United States)
- University of Alberta (Canada)
- University of California, San Francisco (United States)
- National Institute for Medical Research (United Kingdom)
- University of Saskatchewan (Canada)
- Mattapan Community Health Center (United States)
- Reading Hospital Cancer Center (United States)
- Vienna Medical University (Austria)
- Roswell Park Cancer Institute (United States)
- Steiner Medical and Therapeutic Center (United States)
Why no pharmaceutical companies participate in the vitamin D research?
The answer is simple. Vitamin D was discovered many decades ago and cannot be patented. Plus cholecaciferol (vitamin D3) is dirt cheap and currently a 1000 IU capsule of vitamin D retails for as little as 4 cents. Pharmaceutical companies are for-profit enterprises and if they invested money in vitamin D research they would not be able to get sufficient return on their investment. That is why the main hope for the advancement of vitamin D research lies in obtaining funding from government grants and private donations.